
Rover Sojourner
Mission Overview
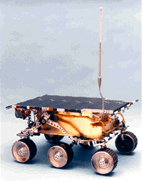
The rover is constrained to a weight of 11.5 kilograms (25.4 lb.). Another
6 kilograms (13.3 pounds) is allocated to lander-mounted rover telecommunications
equipment, structural support of the rover and its deployment mechanisms.
The rover has a normal height of 280 millimeters (10.9 inches), with ground
clearance of 130 mm (5 inches). Its stowage space in the lander allows only
200 mm (7.8 inches) forcing it to squat to a height of 180 mm (7 inches)
when stowed. The rover is 630 mm (24.5 inches) long by 480 mm (18.7 inches)
wide.
Mars Pathfinder will be launched between
Dec. 2, 1996 and December 25, 1996 aboard a Delta
II rocket. The single spacecraft will cruise directly to Mars, enter
the atmosphere with a Viking-derived heat shield and land with the aid of
parachutes, rockets and airbags. Landing is scheduled for July 4, 1997,
on a rocky plain in an area known today as Ares
Vallis.
MFEX is funded by the NASA Office of Advanced Concepts and Technology.
For more information about other Rover subsystems, go to the About the Rover page.
Mission Objectives
The rover is primarily a technology experiment itself, designed to determine
micro-rover performance in the poorly understood Martian terrain so that
future rovers may be designed to be effective in navigating and moving about
the surface of Mars. MFEX has three main mission objectives: technology
experiments, science experiments and mission experiments.
- Technology Experiments
- Mars Terrain Geometry Reconstruction from Imagery
- Mars Basic Soil Mechanics
- Mars Dead Reckoning Sensor Performance and Path Reconstruction/Recovery
- Sinkage in Each Martian Soil Type
- Logging/Trending of Vehicle Performance Data
- Rover Thermal Characterization
- Rover Imaging Sensor Performance
- UHF Link Effectiveness
- Material Abrasion
- Material Adherence
- Rover Science Experiments
- Mission Experiments
- Lander Imaging
- Damage Assesment
Back to the About the Rover Page.
Back to the Rover Home Page.